The crisis in China shakes the stock markets, with possible repercussions worldwide.

The China crisis will have a global impact on financial markets. In this article, we’ll see the 10 companies most at risk of collapse. The deterioration of China’s economic fundamentals, the resulting deflationary pressures and a struggling real estate market are signaling a phase of slower growth for the world’s second-largest economy. This trend will have an impact on a global scale, with particular resonance for multinational companies that depend on China as their primary source of growth.
Chinese monetary policy against the tide
Chinese policymakers are wary of employing debt-financed stimulus to revive an already struggling property market, yet the People’s Bank of China cut interest rates to 3.45% in August. Xi Jinping, China’s leader, has spent years containing the risks of shadow banking and stabilizing a real estate sector that accounted for a sizable chunk of economic activity. Despite some attempts to ease restrictions, economists do not foresee a return to the real estate boom, but rather a gradual reduction in the importance of this sector in the Chinese economy.
Analysts at BNY Mellon IM express concern about the possible scenario for China in 2024, which could prove more challenging than 2023, if economic policy does not provide the necessary support.
They point out that the real estate sector, accounting for about a quarter of China’s GDP, has been the main catalyst for the economic downturn in the country. Its decline has greatly affected overall growth. However, they add that weakening confidence in the private sector may have limited the size of any possible recovery and may have fueled a deflationary spiral.
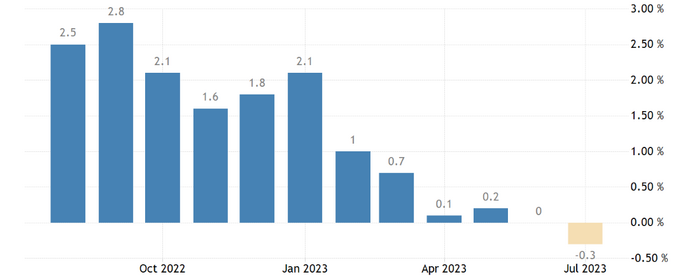
- China’s inflation Year-on-Year
Analysts warn that a prolonged delay in policy support measures and market reforms could put China’s economic prospects at serious risk not only in 2024 but also in subsequent periods.
Top 10 global companies most at risk
The current economic crisis in China could seriously impact global industrial and consumer companies that largely depend on the world’s second-largest economy. This situation presents further challenges for international businesses that have made China their main growth engine, such as raw materials producers in Latin America and Australia. The list of companies with exposure to China is considerable: as many as 200 of the most relevant multinationals in America, Europe, and Japan derive 13% of their revenue from the Chinese market, accumulating a total turnover of 700 billion dollars. This underlines how heavily entire industries are involved in the Chinese economy.
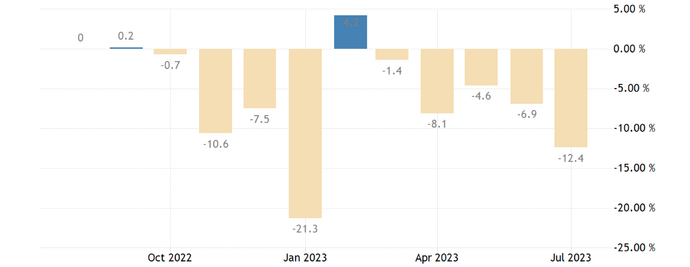
- China’s imports Year-on-Year
Industry and automotive
The decrease in domestic demand in China has a significant impact on key sectors such as automotive and heavy industry. Companies like Caterpillar report lower-than-expected Chinese demand. Geopolitical tensions with the United States are pushing Chinese businesses to reduce their reliance on foreign suppliers, a potential test for global industrial companies.
Tesla is particularly exposed, with around 20% of its sales coming from the Chinese market.
BMW and Porsche are not far behind, as they face not only consumer caution towards large purchases but also growing competition from Chinese companies such as electric car maker BYD, which is conquering market shares in Europe. The weakening of the yuan provides further incentives to local competitors, creating an environment of even fiercer competition. For the two German car companies, around a third of sales come from the Chinese market.
Raw material
Anglo-Australian mining giant Rio Tinto is extremely dependent on China, with more than 50% of its sales concentrated in this market. This makes it one of the most vulnerable companies in the event of a possible global economic downturn. Similarly, other raw materials producers, especially those supplying materials to the construction sector, may experience a decrease in demand: London-listed Anglo American and Chilean copper producer Antofagasta, for example, get about a quarter and a fifth of their sales from China, respectively.
Luxury
Among the companies in the luxury sector most involved with China, we find names such as the Swiss Swatch Group and the Italian Moncler. If Chinese consumer confidence, especially among high-income families, continues to falter, this could also pose a challenge for trusts and wealth management products.
Tourism
Las Vegas Sands (LVS), the US holding company that owns one of the most important hotel-casino chains in the world, generates 68% of its sales from China and has seen its share price fall by almost 10% in the last 30 days.
The effects of the weak yuan
The weakening of the Chinese yuan, which is nearing 15-year lows against the US dollar, is shaking the global economic landscape. While experts predict that China will continue to allow its currency to gradually weaken to support the competitiveness of its exporters, this trend presents significant challenges for international businesses.
The most obvious effect is manifested in the technology and aerospace sectors, where Chinese companies are gaining greater competitiveness. This shift poses a threat to foreign businesses operating in these markets. Additionally, the weak yuan is helping to intensify global competition, putting pressure on companies that rely on China as a key market.
The future of international companies in this context requires an adaptation strategy and a keen eye on the evolving dynamics of the Chinese market. The ability to remain competitive and seize emerging opportunities will become crucial as China continues to redefine its role in the global economy.
In conclusion, the Chinese economic crisis is having a significant impact on businesses globally. Multinational companies and those with a strong economic presence in China face significant challenges as they try to navigate this period of slower growth. The evolving Chinese economic situation will continue to require particular attention from international investors and companies.
Original article published on Money.it Italy 2023-09-08 16:07:00. Original title: Crisi in Cina, le 10 aziende più a rischio




